Saga Pattern for Microservices Distributed Transactions
In this article, we are going to talk about Design Patterns of Microservices architecture which is The Saga Pattern. As you know that we learned practices and patterns and add them into our design toolbox. And we will use these pattern and practices when designing e-commerce microservice architecture.
By the end of the article, you will learn where and when to apply Saga Pattern into Microservices Distributed Architecture with designing e-commerce application system.
Saga Pattern for Distributed Transactions
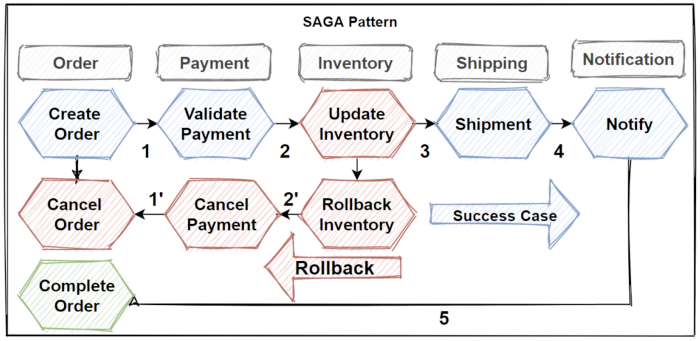
The saga design pattern is provide to manage data consistency across microservices in distributed transaction cases. Basically, saga patterns offers to create a set of transactions that update microservices sequentially,and publish events to trigger the next transaction for the next microservices.
If one of the step is failed, than saga patterns trigger to rollback transactions which is basically do reverse operations with publishing rollback events to previous microservices.
By this way it is manage Distributed Transactions across microservices.As you know that its used some principles inside of the Saga pattern like publish/subscribe pattern with brokers or API Composition patterns.
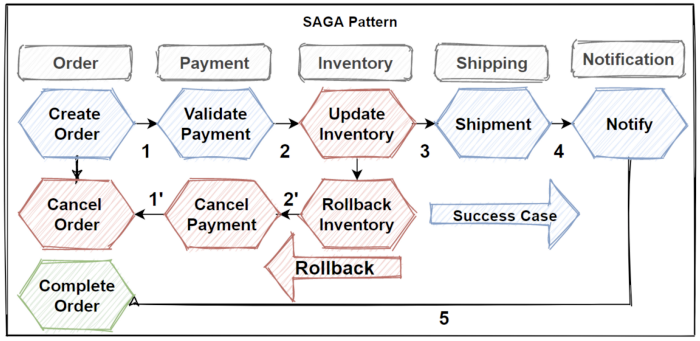
The saga pattern provides transaction management with using a sequence of local transactions of microservices. Every microservices has its own database and it can able to manage local transaction in atomic way with strict consistency.
So saga pattern grouping these local transactions and sequentially invoking one by one. Each local transaction updates the database and publishes an event to trigger the next local transaction.
If one of the step is failed, than saga patterns trigger to rollback transactions that are a set of compensating transactions that rollback the changes on previous microservices and restore data consistency.
There are two type of saga implementation ways, These are “choreography” and orchestration”.
Let me explain Choreography way of Saga pattern.
Choreography Saga Pattern
Choreography provides to coordinate sagas with applying publish-subscribe principles. With choreography, each microservices run its own local transaction and publishes events to message broker system and that trigger local transactions in other microservices.

This way is good for simple workflows if they don’t require too much microservices transaction steps.
But if Saga Workflow steps increase, then it can become confusing and hard to manage transaction between saga microservices. Also Choreography way decouple direct dependency of microservices when managing transactions.
Orchestration Saga Pattern
Another Saga way is Orchestration. Orchestration provides to coordinate sagas with a centralized controller microservice. This centralized controller microservice, orchestrate the saga workflow and invoke to execute local microservices transactions in sequentially.The orchestrator microservices execute saga transaction and manage them in centralized way and if one of the step is failed, then executes rollback steps with compensating transactions.
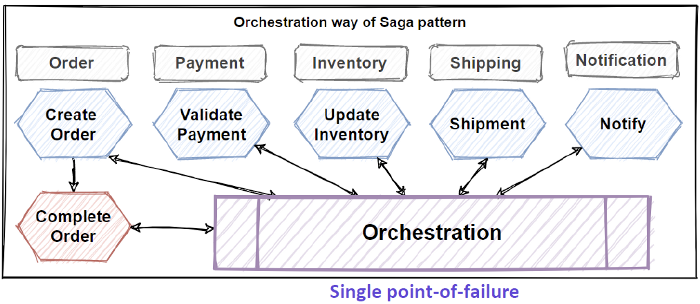
Orchestration way is good for complex workflows which includes lots of steps. But this makes single point-of-failure with centralized controller microservices and need implementation of complex steps.
Rollback of Saga Pattern
The below image shows a failed transaction with the Saga pattern.
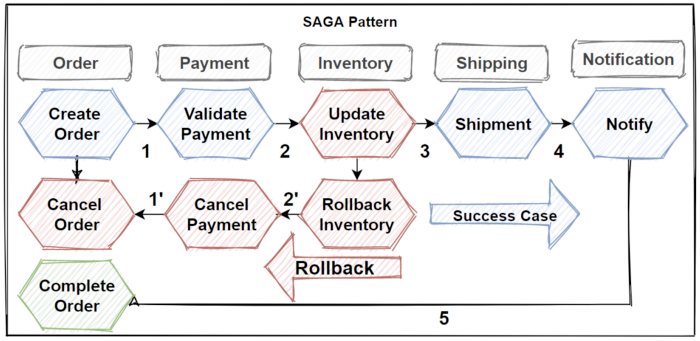
The Update Inventory operation has failed in the Inventory microservice. So when it failed to one step, The Saga invokes a set of compensating transactions to rollback the inventory operations, cancel the payment and the order, and return the data for each microservice back to a consistent state.
We should careful about when using saga pattern in distributed microservices architecture. If our use case required data consistency across several microservices, and required rollback when one of the step is failed, than we should use Saga pattern.
So we should evolve our architecture with applying other Microservices Data Patterns in order to accommodate business adaptations faster time-to-market and handle larger requests.